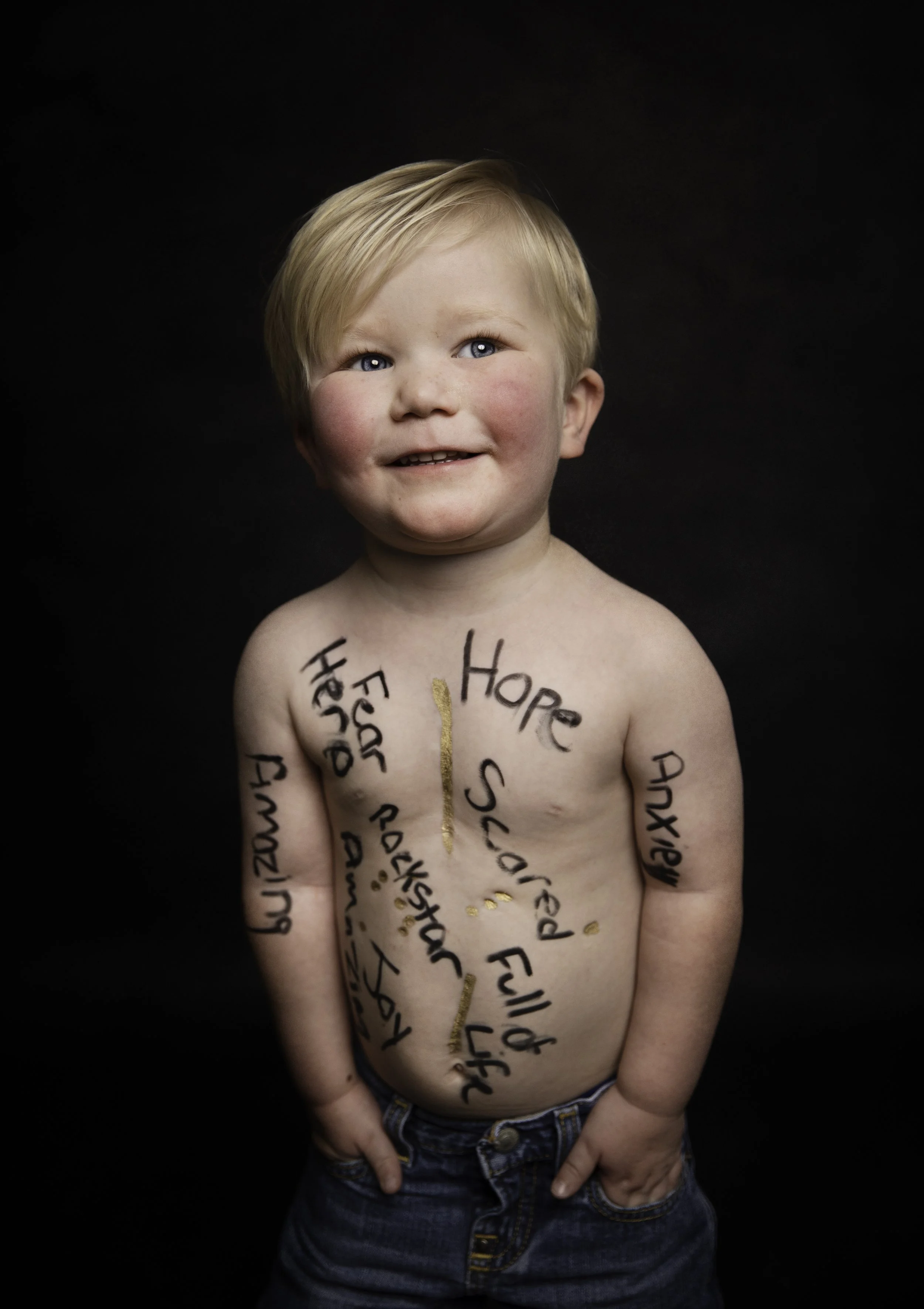
ABOUT CHD
What is CHD?
Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) encompasses all types of heart conditions or disorders present at birth, including both structural defects and any associated complications or diseases that arise from these defects. The term is often used interchangeably with Congenital Heart Defect, which refers specifically to a structural abnormality of the heart that is present at birth. CHDs can vary in severity from minor defects that may not require treatment to complex conditions that need medical or surgical intervention. CHD is the most common birth defect, affecting approximately 1 in 100 babies born wordwide.
THE 1 IN 100
Common Types of Heart Defects.
Congenital heart defects occur in many different forms, depending on which part of the heart is affected. In total, there are over 30 distinct congenital heart defects, each varying in severity and the impact they have on health. Below are eight common types:
-
An ASD is a hole in the wall (septum) that separates the two upper chambers of the heart (the atria). This defect allows oxygen-rich blood to mix with oxygen-poor blood, which can lead to an enlarged heart and increased workload. Some ASDs may close on their own, but others require surgery or catheter-based procedures.
-
A VSD is a hole in the wall between the two lower chambers of the heart (the ventricles). This defect causes blood to flow abnormally between the ventricles, which can result in heart failure or pulmonary hypertension if not treated. VSDs vary in size and may require surgical repair.
-
PDA is a condition where a blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth, allowing blood to flow improperly between the aorta and the pulmonary artery. In some cases, the ductus closes on its own, but others may require medication or surgery.
-
Truncus arteriosus is a rare congenital heart defect where the main artery (truncus) that carries blood from the heart to the body and lungs does not properly separate into two separate arteries: the pulmonary artery and the aorta
-
TOF is a complex congenital heart defect that involves four heart abnormalities: a ventricular septal defect (VSD), pulmonary stenosis (narrowing of the pulmonary valve or artery), an overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy (thickening of the right ventricle). TOF often causes cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin) and requires surgical intervention early in life.
-
Coarctation is a narrowing of the aorta, the large blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. This defect can lead to high blood pressure and heart damage. Surgery is usually required to correct the narrowing.
-
In TGA, the positions of the two main arteries leaving the heart—the pulmonary artery and the aorta—are reversed. This condition causes oxygen-poor blood to circulate through the body, while oxygen-rich blood is sent back to the lungs. TGA is a life-threatening condition that typically requires surgery soon after birth.
-
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome (HRHS) is a rare congenital heart defect where the right side of the heart, particularly the right ventricle, is underdeveloped. This results in an inadequate blood flow to the lungs, leading to low oxygen levels in the body.
ABOUT CHD
Facts & Stats.

CHD affects 1 in 100 live births worldwide, making it the most common type of birth defect

There are an estimated 1.4 million adults in the U.S. living with CHD, a number that is expected to increase by over 30% by 2030

Despite being the leading cause of birth defect-related deaths, CHD receives significantly less research funding compared to other medical conditions. In 2020, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) allocated less than $40 million for CHD research, whereas conditions like cancer and diabetes receive billions in research funding annually

1 in 10 children with CHD will not live until adulthood

The lifetime medical costs for an individual with CHD can exceed $1 million. This includes surgeries, hospitalizations, medications, and long-term care

Around 50% of congenital heart defects are diagnosed after birth, often because the symptoms are subtle or mistaken for other conditions. Late diagnosis can delay treatment and worsen outcomes, especially for complex defects

More than 1/3 of children with CHD are diagnosed or treated for a mental health condition by 18 years of age

Studies indicate that 1 in 3 adults with CHD will require significant medical interventions such as valve replacements, arrhythmia treatment, or even a heart transplant later in life

An approximate 100-200 deaths each year are due to unrecognized heart disease in newborns. These numbers exclude those dying before diagnosis

Nearly 40,000 infants in the U.S. are born each year with CHDs

CHD is 60 times more common than all childhood cancers combined

Individuals with congenital heart disease and their families are at a higher risk of developing anxiety, depression, and PTSD due to the emotional and physical challenges of living with a chronic condition

Approximately 25% of children born with a CHD will need open heart surgery within their first year of life to survive

A child is born with CHD every 15 minutes

Most causes of CHDs are unknown. Only 15-20% of all CHDs are related to known genetic conditions

CHDs are as common as autism and about 25 times more common than cystic fibrosis

A newborn with CHD will need an average of 3.2 surgeries in their lifetime. Many will undergo more